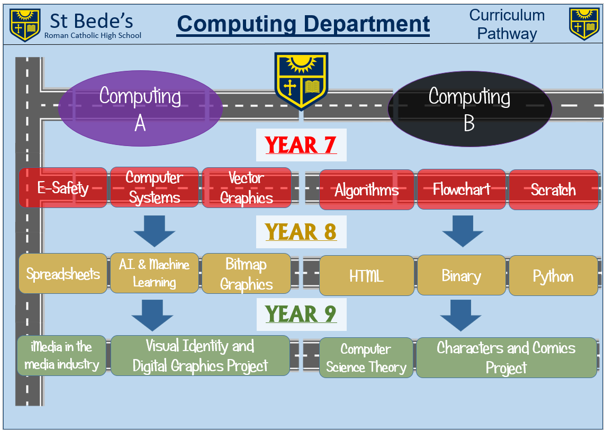
Our Year 9 Computing curriculum prepares students for the transition into KS4 study by combining theoretical knowledge with project-based learning. Students explore the impact of computing on society, develop advanced programming skills, and engage in creative digital media projects. By working through extended assignments split into two parts, they experience a more professional design and development process, building resilience, independence, and technical expertise. This approach ensures that students are ready to meet the challenges of formal qualifications in Computing.
9.1 iMedia in the Media Industry
Students will gain an insight into the media industry and the importance of pre-production planning. They will learn about work planning, teamwork, and resource management, before moving on to design documents such as storyboards, wireframes, and scripts. This unit helps students to understand how ideas are developed and communicated within media projects. The unit ends with a written assessment, marked out of 20.
9.2 Visual Identity and Digital Graphics Project (Part 1)
Students will begin a creative project focused on building a visual identity. They will interpret client briefs, design mood boards, and create annotated sketches of logos. Using their ideas, they will design and produce a visual identity for a given brand. This project is assessed through a practical task, marked out of 20.
9.2 Visual Identity and Digital Graphics Project (Part 2)
In the second half of this project, students will further develop their design skills. They will use pre-production documents such as mind maps and visualisation diagrams to plan their work and prepare assets for digital editing. They will then create and refine their final product, applying advanced editing techniques to improve quality. The project concludes with an assessment, marked out of 20.
9.3 Computer Science Theory
Students will explore the impact of computing on society, considering legal, ethical, and environmental issues. They will learn about computing legislation, ethical challenges, and the environmental effects of technology. The unit concludes with a debate, allowing students to develop their critical thinking and communication skills. The unit is assessed through a written paper, marked out of 20.
9.4 Characters and Comics Graphics Project (Part 1)
Students will begin by exploring pre-production documents and interpreting client briefs. They will then use Adobe Fireworks tools such as the pen tool and convert marquee to path to design and create comic-style characters and objects. The project is assessed through a creative task, marked out of 20.
9.4 Characters and Comics Graphics Project (Part 2)
In the second half of this project, students will design storyboards, create panel backgrounds and layouts, and add dialogue to bring their comic stories to life. They will also evaluate their finished product, suggesting improvements to enhance their work. This project is assessed through a practical evaluation, marked out of 20.