Students at St. Bede’s study topics across all three disciplines of science from year 7 through to year 11; these are biology chemistry and physics. The coverage of these topics provides students with a breadth and depth of understanding of the world around them. Biology helps students to understand the living world and organisms, covering the biological processes of humans, other animal, plants and microorganisms. In chemistry, students gain an understanding of the atoms, elements and molecules which make up matter and the chemical processes which take place to form new substances. In physics, students gain an understanding of energy and forces, how these interact on Earth and beyond, to make sense of actions we see every day.
Year 7
In year 7, students are taught a breadth of topics across all three specialisms of biology, chemistry and physics. The schemes of learning across year 7-9 are designed to cover all topics outlined in the KS3 national curriculum for science. These topics are interleaved to ensure regular revisiting of each specialism throughout the year. The topics are chosen as the fundamental scientific concepts of many topics they will be taught in subsequent years of key stage 3 and key stage 4.
Due to the practical nature of the subject, topics are taught on a rotation basis as seen in the table below. The content of each topic can be seen below the table.
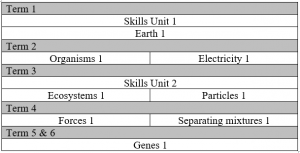
Skills Unit 1
- Using apparatus safely
- Assessing risks in investigations
- Planning investigations, including variables
- How to process collected data, including graph skills
- Writing appropriate scientific methods
- Drawing and interpreting line graphs
Skills Unit 2
- Calculating means and looking for repeatable data
- Method writing and including scientific equipment
- Drawing a table appropriate for a practical
Earth 1 – Chemistry
- The structure of the earth
- Formation and types of rocks
- The rock cycle
- The earth and solar system
- The moon
Organisms 1 – Biology
- Levels of organisation
- The skeleton, joints and muscles
- Using microscopes
- Plant and animal cells
- Unicellular and multicellular organisms
- Specialised cells
- Transport into and out of cells
Electricity 1 – Physics
- Current and Potential difference
- Resistance
- Series and parallel circuits
- Using electricity equations
Matter 1: The Particle Model – Chemistry
- States of matter
- State changes
- Boiling and Evaporation
- Diffusion
- Gas pressure
Ecosystem 1 – Biology
- Food chains and food webs
- Ecosystems and interdependence
- Competition for resources
- Plant reproduction
- Plant fertilisation and germination
Forces 1 – Physics
- Gravity
- Balanced and unbalanced forces
- Laws of motion
- Speed, distance & time
Matter 1: Separating Mixtures – Chemistry
- Pure and impure substances
- Making solutions
- Solubility
- Filtration
- Distillation and evaporation
- Chromatography
Genes 1 – Biology
- Variation
- Adaptations of plants and animals
- Adolescence
- Reproductive systems
- Development of a foetus
- The menstrual cycle
Additional Information
As part of each unit covered throughout the year, students are given many opportunities to develop their scientific and skills throughout each unit. In a similar manner to how required practicals are now part of many topics in GCSE, we have woven required practicals into units of our key stage 3 units to maximise the development of scientific skills in the topics we deliver.
Year 8
In year 8, students are taught a breadth of topics across all three specialisms of biology, chemistry and physics. The schemes of learning across year 7-9 are designed to cover all topics outlined in the KS3 national curriculum for science. These topics are interleaved to ensure regular revisiting of each specialism throughout the year. The topics are chosen as the fundamental scientific concepts of many topics they will be taught in subsequent years of key stage 3 and key stage 4.
Due to the practical nature of the subject, topics are taught on a rotation basis as seen in the table below. The content of each topic can be seen below the table.
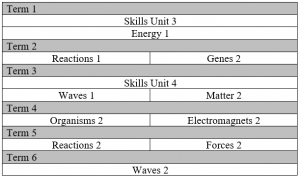
Skills Unit 3
- Look for anomalies and calculating means
- Looking for patterns in data
- Interpreting graphs
Skills Unit 4
- Drawing appropriate graphs
- Sampling and extrapolating data
- Writing and evaluating methods
Energy 1 – Physics
- Food as fuel
- Energy resources
- Power ratings and calculations
- Energy transfer and dissipation
Reactions 1 – Chemistry
- Acids and alkalis
- Neutralisation
- Metals and non-metals
- Chemical reactions of metals
- Displacement reactions
Genes 2 – Biology
- Inheritance
- DNA
- Genetics
- Evolution and natural selection
- Extinction
- Preserving biodiversity
Waves 1 – Physics
- Sound waves
- Hearing
- Light
- Reflection and refraction
- The eye and vision
- Observing colour
Matter 2 – Chemistry
- Atomic Structure
- Compounds
- Chemical formulae
- The Periodic Table
Organisms 2 – Biology
- Breathing system
- Gas exchange
- Alcohol, drugs and smoking
- Nutrients and healthy diet
- Digestive system
- Enzymes
Electromagnet 2 – Physics
- Magnetic Materials
- Induced and permanent magnets
- Electromagnets
Reactions 2 – Chemistry
- Combustion
- Thermal decomposition
- Endothermic & exothermic reactions
Forces 2 – Physics
- Friction and Drag
- Turning and moments
- Pressure in solids, liquids and gases
Waves 2 – Physics
- Light waves
- Sound waves
- Ultrasound
- The Ear
- Microphones & loud speakers
Additional Information
As part of each unit covered throughout the year, students are given many opportunities to develop their scientific and skills throughout each unit. In a similar manner to how required practicals are now part of many topics in GCSE, we have woven required practicals into units of our key stage 3 units to maximise the development of scientific skills in the topics we deliver.
Year 9
In year 9, students are taught a breadth of topics across all three specialisms of biology, chemistry and physics. The schemes of learning across year 7-9 are designed to cover all topics outlined in the KS3 national curriculum for science. These topics are interleaved to ensure regular revisiting of each specialism throughout the year. The topics are chosen as the fundamental scientific concepts of many topics they will be taught in subsequent years of key stage 3 and key stage 4.
Due to the practical nature of the subject, topics are taught on a rotation basis as seen in the table below. The content of each topic can be seen below the table.
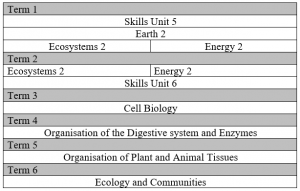
Skills Unit 5
- Collecting data and considering resolution of equipment
- Identifying resolution of equipment
- Calculating uncertainty
Skills Unit 6
- Drawing graphs with decimal scales and negative scales
- Describing graphs and reading off values
- Extrapolating graphs and making predictions
Earth 2 – Chemistry
- The carbon cycle
- Global warming
- Climate change
- Using Earth’s resources
- Recycling
Ecosystems 2 – Biology
- Aerobic and anaerobic respiration
- Biotechnology
- Photosynthesis
- Adaptations of plants
- Plant minerals
Energy 2 – Physics
- Machines and work
- Energy transfer: Conduction, convection, radiation
Cell Biology
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Organelles in plant, animal and bacterial cells
- Microscopy and methods of using microscopes
- Using the magnification equation
- Stem cells and cell differentiation
- Meristems
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Active Transport
- Mitosis and the cell cycle
- Therapeutic cloning
Organisation of the Digestive System and Enzymes
- Cells, tissues and organs
- The digestive system
- Basic structure of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
- Food tests reagent and results
- Enzymes (lipase, amylase and protease)
- pH and the effect on digestion
Organisation of Plant and Animal Tissue
- The lungs
- The components of blood
- The structure of the heart Helping the heart (pacemakers, stents, statins and heart transplants)
- The structure of a leaf and the roles of the tissues
- Stomata and guard cells
- Transpiration
Ecology and Communities
- Biotic and Abiotic factors
- Sampling (random and transect)
- Competitions in plants and animals
- Food webs and food chains
- The carbon cycle
- The water cycle
Human Population growth - Land pollution
- Water pollution and Eutrophication
- Atmospheric pollutants
- The greenhouse effect
- The impact of climate change
- Maintaining Biodiversity
Additional Information
As part of each unit covered throughout the year, students are given many opportunities to develop their scientific and skills throughout each unit. In a similar manner to how required practicals are now part of many topics in GCSE, we have woven required practicals into units of our key stage 3 units to maximise the development of scientific skills in the topics we deliver.
Year 10
A large proportion of the year group study combined sciences which encompasses a broad range of topics for biology, chemistry and physics according to the GCSE combined science specifications. A group of students study separate sciences, which covers additional content for each specialisms; these are highlighted in red in the curriculum map below. Within this, students develop a wide range of mathematical skills and practical skills to plan, deliver and process data from practical investigations.
Unit 1 – Atoms, The Periodic Table & Bonding – Chemistry
- Separation techniques
- Atomic structure
- Historic development of the atomic model
- The periodic table
- Historic discoveries of the periodic table
- States of matter
- Ions and ionic bonding
- Covalent bonding and covalent structures
- Allotropes of carbon
- Metallic bonding
- Nanotechnology
Unit 2 – Energy & Energy Generation – Physics
- Energy transfer
- Infrared radiation
- Specific heat capacity
- Required practical: specific heat capacity
- Insulation to prevent energy loss
- Required practical: thermal insulators
- Energy demands
- Renewable energy sources
Unit 3 – Diseases and Prevention – Biology
- Health and disease
- Pathogens causing disease
- Required practical: growing bacterial cultures
- Preventing bacterial growth
- Preventing infections
- Viral, bacterial, fungal and protest diseases
- Human defences
- Plant diseases and defences
- Vaccinations
- Drugs: examples, discovery and development
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Non-communicable diseases
- Lifestyle affecting diseases
Unit 4 – Quantitative Chemistry & Metal Reactions – Chemistry
- Relative masses and moles
- Reacting masses calculations
- Percentage yield and atom economy
- Concentrations
- Titrations
- Required practical: titrations
- Volumes of gases
- The reactivity series and displacement reactions
- Extracting metals
- Making salts, pH and neutralisation
- Electrolysis and metal extraction
- Required practical: electrolysis
Unit 5 – Electrical Circuits and Safety, Matter & Radioactivity – Physics
- Electrical circuits
- Electrical components
- Required practical: Series and parallel circuits
- Required practical: component characteristics
- Alternating current and power stations
- Cables and plugs
- Electrical power and energy transfer
- Electrical appliances and efficiency
- Density
- Required practical: density
- Changes of state
- Internal energy
- Specific latent heat
- Gas pressure and temperature
- Gas pressure and volume
- Atoms and radiation
- Radioactive decay
- Ionising radiation
- Activity and half-life
- Nuclear radiation in medicine
- Nuclear fusion and fission
Unit 6 – Bioenergetics & Homeostasis – Biology
- Photosynthesis
- Required practical: rate of photosynthesis
- Uses of glucose in the plant
- Industrial plant growth and photosynthesis
- Aerobic and anaerobic respiration
- Biotechnology in food and drink
- Body responses to exercise
- Metabolism and the liver
- Homeostasis and negative feedback
- The nervous system
- Required practical: measuring reaction time
- The brain
- The eye and problems with vision
- The endocrine system
- Glucoregulation and diabetes
- The human reproductive system
- Controlling fertility and infertility treatments
- Plant hormones and commercial uses
- Required practical: measuring the effect of light or gravity on seed germination
Unit 7 – Energy Changes and Rate of Reaction – Chemistry
- Exothermic and endothermic reactions
- Required practical: temperature changes
- Reaction profiles
- Bond energy calculations
- Fuels and chemical cells
- Factors affecting rates of reactions
- Required practical: Concentration & rate of reaction
- Reversible reactions
- Dynamic equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s principle
- Fractional distillation
- Combustion and cracking of hydrocarbons
Additional Information
The GCSE course is started in February of year 9 to allow the coverage of all units by April of year 11. The year 10 course continues on from the topics covered at the end of year 9. The topics are sequenced where biology, chemistry and physics topics are interleaved to build on a previous topic covered and to regular revisit each specialism. The topics highlighted in italics are those covered in the separate sciences only.
Year 11
Most of the year group study combined sciences which encompasses a broad range of topics for biology, chemistry and physics according to the GCSE combined science specifications. A group of students study separate science, which covers additional content for each specialisms; these are highlighted in italics in the curriculum map below. Within this, students develop a wide range of mathematical skills and practical skills to plan, deliver and process data from practical investigations. Required practical opportunities are highlighted in bold.
Unit 8 –Rate of Reaction – Chemistry
- Factors affecting rates of reactions
- Required practical: Concentration & rate of reaction
- Reversible reactions
- Dynamic equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s principle
- Fractional distillation
- Combustion and cracking of hydrocarbons
Unit 9 – Forces and Motion – Physics
- Vector and scalar quantities
- Resultant forces
- Moments and levers
- Equilibrium
- Parallelogram and resolution of forces
- Velocity and acceleration
- Motion graphs
- Forces and accelerations
- Terminal velocity
- Momentum
- Conservation of momentum
- Impact forces and safety
- Forces and elasticity
- Required practical: force and extension
- Force and pressure
Unit 10 – Reproduction, Genetics and Evolution – Biology
- Sexual and asexual reproduction
- Cell division (meiosis and mitosis)
- Reproduction in other organisms
- DNA and the genome
- Protein synthesis
- Gene expression and mutations
- Predicting inheritance
- Inherited diseases and screening processes
- Variation in species
- Evolution and natural selection
- Selective breeding
- Genetic engineering
- Cloning
- Ethics of gene technologies
- Theories of evolution
- Evidence for evolution
- Antibiotic resistance
- Classification systems
Unit 11 – Organic Chemistry and Polymers – Chemistry
- Reactions of alkenes
- Alcohols and carboxylic acids
- Esters
- Polymerisation
- Natural polymers and DNA
Unit 12 – Chemical Analysis and the Earth’s Atmosphere and Resources – Chemistry
- Purity of substances
- Chromatography
- Required practical: analysing chromatograms
- Required practical: identifying unknown compounds
- Testing for gases
- The earth’s atmosphere (previous and current)
- Greenhouse gases and climate change
- Atmospheric pollutants
- Finite and renewable resources
- Potable water and water treatment
- Required practical: analysing water samples
- Extracting metals from ores and the earth
- Reduce, reuse and recycle
Unit 13 – Electromagnetic Spectrum and Electromagnetism – Physics
- Waves
- Required practical: investigating wave properties
- Reflection and refraction
- Properties of light
- Required practical: reflection and refraction
- Lenses
- Sound waves and ultrasound
- Seismic waves
- The electromagnetic spectrum and uses
- Required practical: investigating infrared radiation
- Communications using waves
- Waves in medicine
- Magnetic fields
- Electromagnets in devices
- The motor effect
- The generator effect
- Transformers
Unit 14 – Ecology and Biodiversity – Biology
- Communities and interdependence
- Required practical: organism distribution
- Competition for survival and adaptations
- Feeding relationships
- The carbon cycle
- Rates of decomposition
- Required practical: rates of decay
- Human population
- Land, air and water pollution
- Deforestation and global warming
- Maintaining biodiversity
- Sustainable living and food production
Unit 15 – Space – Physics
- Solar system
- Life-cycle of stars
- Satellites and orbits
- The expanding universe
- Origins of the universe
Additional Information
The GCSE course is started in February of year 9 to allow the coverage of all units by April of year 11. The year 11 course continues on from the topics covered in year 9 and 10. The topics are sequenced where biology, chemistry and physics topics are interleaved to build on a previous topic covered and to regular revisit each specialism. The topics highlighted in red are those covered in the separate sciences only.
Equipped with his five senses, man explores the universe around him and calls the adventure Science
Edwin Powell Hubble

